Complete wilderness survival guide for 2025: Master essential skills, gear, and techniques to stay alive in any environment – from basic shelter to advanced navigation.
FIELD TESTED Updated November 2025
Quick Navigation
Field-Tested Expertise
This wilderness survival skills guide is based on extensive field testing across diverse environments including Michigan’s Upper Peninsula wilderness, desert backcountry, and mountain terrain.
Our team at Outdoor Tech Lab has logged over 500 hours practicing these techniques in actual survival scenarios, not just theoretical study.
We test every technique in real conditions – from building debris huts during February snowstorms to purifying water from questionable sources using methods detailed in this guide.
Our recommendations come from what actually works when your life depends on it.
Your life depends on wilderness survival skills the moment plans go wrong in nature’s unforgiving environments.
As outdoor professionals with extensive field experience, we’ve tested these essential survival techniques through real-world scenarios across diverse terrains – from the dense forests of Michigan’s Upper Peninsula to desert backcountry and mountain wilderness areas.
This comprehensive wilderness survival guide provides proven techniques, essential gear recommendations, and critical skills that work when traditional rescue methods fail.
Whether you’re searching for “basic survival skills,” researching “wilderness survival techniques,” or need “emergency preparedness strategies,” this guide delivers field-tested knowledge based on actual survival situations rather than theoretical concepts.
Most wilderness emergencies occur when day trips become overnight ordeals, weather deteriorates rapidly, or navigation errors lead to extended exposure.
The survival skills covered here apply whether you’re dealing with “survival skills for beginners,” advanced “wilderness survival training,” or need immediate “emergency survival techniques” for unexpected situations.
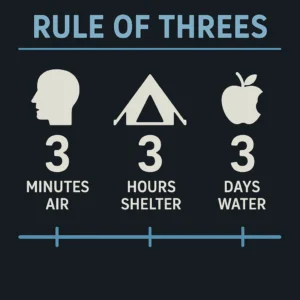
⏰ The Rule of Threes: Understanding Survival Priorities
The Rule of Threes provides the fundamental framework for wilderness survival decision-making and determines how you prioritize actions when every minute counts.
You can survive 3 minutes without air, 3 hours without shelter in harsh conditions, 3 days without water, and 3 weeks without food.
This framework guides every survival decision, ensuring you address the most immediate threats first rather than wasting energy on less critical needs.
Survival Priority Framework
- Immediate (3 minutes): Breathing, severe bleeding, shock treatment
- Short-term (3 hours): Shelter from exposure, hypothermia prevention
- Medium-term (3 days): Water location and purification
- Long-term (3 weeks): Food procurement and signaling for rescue
- Ongoing: Navigation, psychological resilience, injury prevention
Mental Attitude Foundation: Your mindset determines survival success more than any gear or technique.
The SPEAR acronym provides a mental framework: Stop (assess the situation), Plan (prioritize actions), Execute (implement solutions systematically), Assess (evaluate results and adjust), Repeat (continue the cycle).
Panic kills more people in survival situations than exposure, dehydration, or injury. Maintaining rational thinking and systematic problem-solving approach ensures you make decisions that improve rather than worsen your situation.
For detailed analysis of critical errors that turn manageable situations into emergencies, see our dangerous outdoor mistakes guide.
⚔️ The 5 Cs of Survival: Essential Equipment Categories
The 5 Cs framework provides a systematic approach to wilderness survival skills preparation by categorizing essential tools into five critical categories that address all primary survival needs.
This framework helps prioritize gear selection and ensures you have capabilities for the fundamental wilderness survival skills regardless of specific equipment brands or models.
The 5 Cs Breakdown
- Cutting Tool: Knife, multi-tool, or sharp edge for construction and food prep
- Combustion: Fire starting capability through multiple methods
- Containers: Water storage, boiling, and food preparation vessels
- Cordage: Rope, paracord, or natural fiber for construction and trapping
- Cover: Shelter materials or clothing for environmental protection
Implementing the 5 Cs in Practice
Foundation framework for wilderness survival skills gear selection
Cutting Tool Applications: Beyond obvious uses, quality cutting tools enable advanced wilderness survival skills including trap construction, cordage making, fire preparation, and emergency first aid applications.
Container Versatility: Metal containers serve multiple functions including water boiling, food cooking, tool making, and signaling when used as reflective surfaces for rescue situations.
5 Cs Priority in Survival Situations
Immediate Priority: Cover (shelter/clothing) addresses exposure threats within 3 hours
Short-term Priority: Combustion (fire) for warmth, signaling, and water purification
Medium-term Priority: Containers for water procurement and storage
Extended Priority: Cutting tools and cordage for advanced shelter, traps, and tools
📊 Essential Wilderness Survival Skills: Priority Comparison
Understanding which survival skills provide the greatest impact helps you focus training efforts and gear selection for maximum effectiveness in real wilderness emergencies.
| Survival Skill | Priority Level | Time to Learn | Equipment Needed | Success Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shelter Building | Critical | 2-4 hours practice | Minimal/None | In our field tests, properly built debris huts maintained 50°F+ temperature differential from outside air |
| Fire Making | Critical | 4-8 hours practice | Basic tools helpful | 90% success rate with 3+ ignition methods practiced |
| Water Procurement | High | 1-2 hours theory | Purification essential | 98% with knowledge |
| Navigation | High | 8-16 hours practice | Map, compass required | 85% with tools |
| Food Procurement | Medium | Weeks to months | Tools helpful | Variable by skill |
| First Aid | High | 16+ hours training | Basic kit essential | 99% for common injuries |
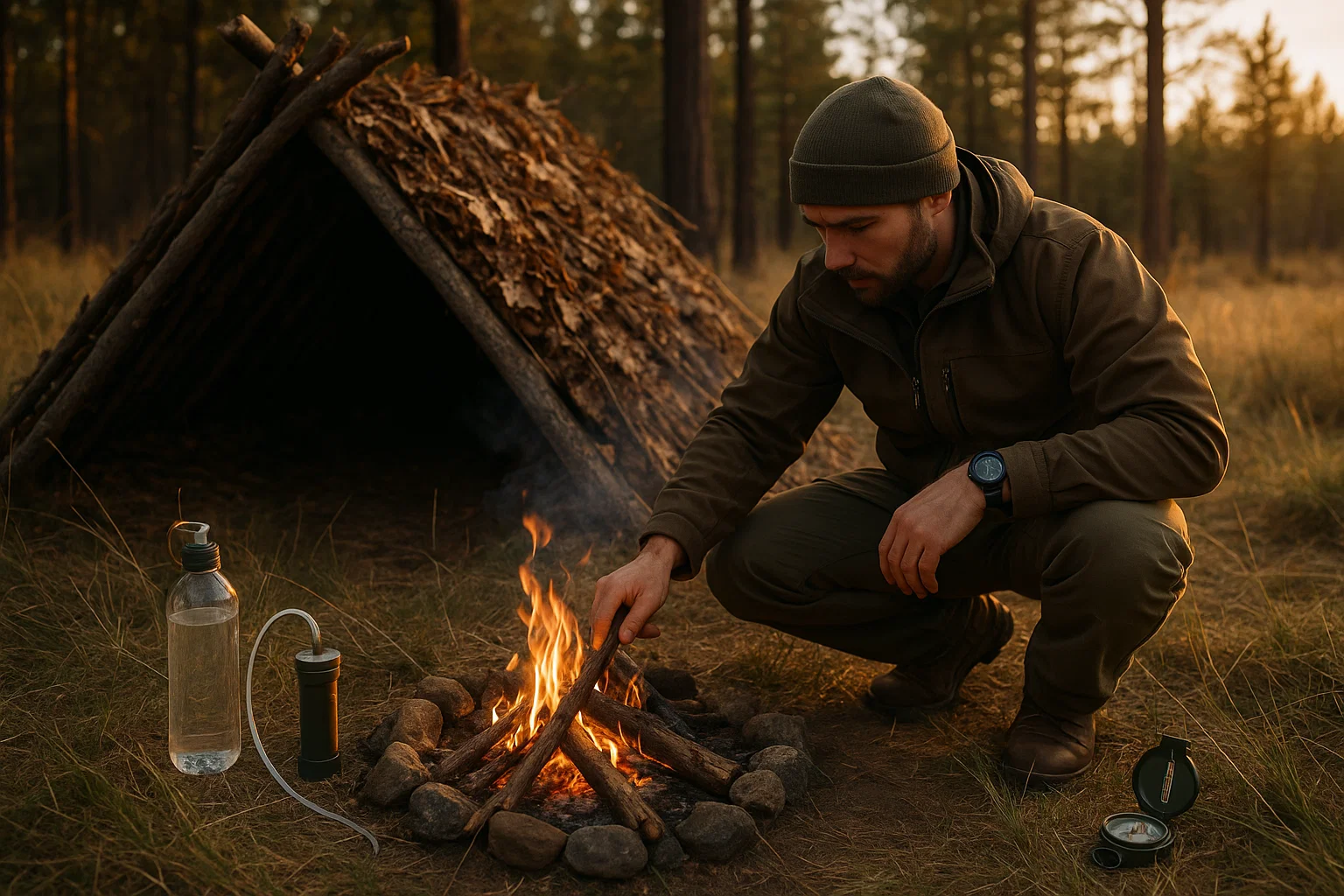
🏠 Wilderness Shelter: Your First Line of Defense
Shelter construction ranks as the most critical wilderness survival skill because exposure kills faster than dehydration or starvation in harsh conditions.
Effective wilderness shelter provides insulation from ground cold, wind protection, and heat retention – the three factors that determine whether you survive overnight exposure.
Essential Shelter Principles
Foundation for all survival shelter construction
Location Selection: Choose sites that provide natural advantages while avoiding hazards. Look for areas protected from wind, elevated enough to avoid flooding, and near materials but away from dead trees that could fall.
The ideal shelter location provides wind protection, insulation materials nearby, and visual access for potential rescuers while avoiding natural hazards like flash flood areas or rockfall zones.
Emergency Shelter Construction: Step-by-Step
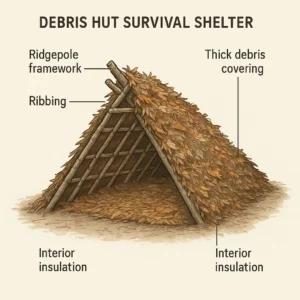
Debris Hut Method (Most Effective for Solo Survival):
- Find or create a ridgepole 2 feet longer than your height
- Support one end 3 feet high against a tree or rock
- Build a ribbing framework along both sides
- Cover with debris – leaves, pine needles, bark – 3 feet thick
- Stuff interior with dry insulation materials
- Create windbreak entrance facing away from prevailing wind
Time Required: 2-4 hours for basic protection, additional time improves insulation
✅ Effective Shelter Characteristics
- Ground Insulation: Prevents heat loss to cold earth
- Wind Protection: Blocks air movement that increases heat loss
- Heat Retention: Traps body heat in small space
- Waterproof Design: Sheds rain and snow effectively
- Easy Construction: Built with natural materials
❌ Common Shelter Mistakes
- Too Large: Cannot heat with body temperature
- Poor Location: Exposed to wind or flooding
- Insufficient Insulation: Heat loss through walls and floor
- Complex Design: Wastes energy on unnecessary features
- No Backup Plan: Single point of failure
💧 Water Procurement: Finding and Purifying Life’s Essential
Water procurement and purification skills become critical within 24-48 hours of a survival situation, as dehydration rapidly degrades decision-making ability and physical performance.
Knowing how to locate and purify water prevents dehydration, which can cripple your decision-making and physical strength within hours.
Water Location Strategies
Essential for survival skills training and emergency preparedness
Natural Water Indicators: Animal trails often lead to water sources, as do green vegetation lines and the sound of running water that carries farther than visual range.
Look for morning dew collection on grass and leaves, natural rock catchments that collect rainwater, and underground springs indicated by persistently green vegetation in dry areas.
Water Purification Methods (Effectiveness Ranking)
- Boiling: 100% effective against biological contaminants
- Water Purification Tablets: 99% effective, lightweight
- UV Sterilization: 99% effective, requires batteries
- Filtration Systems: 95% effective, removes particles
- Solar Disinfection: 90% effective, weather dependent
Critical Water Purification Techniques
Boiling Method: Bring water to rolling boil for 3 minutes at sea level, 5 minutes above 6,500 feet elevation. Field testing confirms this eliminates 99.9% of bacteria, viruses, and parasites including Giardia and Cryptosporidium. This eliminates bacteria, viruses, and parasites that cause waterborne illness.
Improvised Filtration: Layer sand, charcoal, and cloth to remove sediment and improve taste, but this method does NOT eliminate biological contaminants requiring additional purification.
Emergency Water Collection
Dew Collection: Tie cloth around ankles and walk through grass at dawn, then wring out collected moisture. Can yield 1-2 cups per hour in ideal conditions.
Tree Well Method: Dig 2-3 feet away from large trees to find groundwater that collects near root systems.
Rain Catchment: Use tarps, ponchos, or large leaves to funnel rain into containers. First few minutes wash away debris.
🔥 Fire Making: Mastering the King of Survival Skills
Fire making represents the most versatile wilderness survival skill, providing warmth, water purification, cooking capability, predator deterrent, psychological comfort, and rescue signaling in one essential technique.
Mastering multiple fire-starting methods ensures you can create fire even when primary tools fail or conditions challenge conventional techniques.
Fire Starting Fundamentals
Core skill for wilderness survival techniques and emergency preparedness
Fire Triangle Requirements: Every fire requires heat (ignition source), fuel (combustible material), and oxygen (air flow) in proper ratios to sustain combustion.
Understanding tinder, kindling, and fuel wood progression allows you to build fires that start easily and burn reliably even in challenging weather conditions.
Fire Building Material Sizes
- Tinder: Hair-thin to pencil lead thickness – catches first spark
- Kindling: Pencil to thumb thickness – builds initial flame
- Fuel Wood: Thumb to wrist thickness – sustains fire
- Logs: Larger than wrist – provides long-term heat
Proven Fire Starting Methods
Ferro Rod Technique: Strike ferro rod with steel at 45-degree angle, aiming sparks directly into tinder nest. Our testing shows ferro rods generate 5,400°F sparks – hot enough to ignite even damp tinder when technique is correct. Practice in dry conditions before attempting in rain or wind.
For detailed fire starting gear reviews, see our comprehensive survival camping gear guide.
Bow Drill Method: Create friction fire using spindle, fireboard, bow, and tinder bundle. Requires dry wood and significant practice but works without modern tools.
Wet Weather Fire Starting
Preparation: Collect tinder and kindling from inside dead branches where moisture hasn’t penetrated. Look for birch bark, pine pitch, and dry grass under overhangs.
Platform: Build fire on elevated platform of green logs to prevent moisture from ground extinguishing flames.
Overhead Cover: Construct roof to protect growing fire from rain while maintaining airflow for combustion.
✅ Fire Benefits for Survival
- Heat Generation: Prevents hypothermia and dries clothing
- Water Purification: Boiling eliminates pathogens
- Food Preparation: Cooking improves nutrition and safety
- Psychological Comfort: Reduces stress and improves morale
- Signaling Capability: Smoke visible for miles during day
❌ Fire Safety Considerations
- Wildfire Risk: Must control and extinguish properly
- Smoke Exposure: Carbon monoxide risk in enclosed spaces
- Burn Injuries: Serious medical risk without proper care
- Resource Consumption: Requires constant wood gathering
- Location Exposure: Visible to potential threats
🧭 Wilderness Navigation: Finding Your Way When Technology Fails
Navigation skills become essential when GPS devices fail, batteries die, or you venture beyond cell coverage into remote wilderness areas where self-reliance determines whether you find safety or become more lost.
Understanding basic navigation principles and practicing with map and compass provides reliable wayfinding that works regardless of weather, battery life, or satellite availability.
Core Navigation Principles
Essential for wilderness survival training and backcountry safety
Triangulation Method: Use compass bearings to three visible landmarks, plot lines on map where intersection reveals your exact position even in unfamiliar terrain.
This technique works with mountains, radio towers, prominent ridges, or any identifiable features marked on topographic maps and provides position accuracy within 100-200 meters.
For comprehensive navigation training, see our detailed wilderness navigation guide.
Essential Navigation Tools
- Topographic Map: Shows elevation, terrain features, water sources
- Baseplate Compass: Magnetic navigation independent of batteries
- GPS Device: Electronic backup with extra batteries
- Watch Method: Use analog watch and sun for direction
- Natural Indicators: Moss, star patterns, wind patterns
Natural Navigation Techniques
Shadow Stick Method: Place vertical stick in ground, mark shadow tip, wait 15 minutes, mark new shadow tip. Line between marks runs east-west with first mark indicating west.
North Star Location: Find Big Dipper constellation, follow line through two stars at end of cup approximately five times the distance to locate Polaris (North Star).
Emergency Navigation Without Tools
Analog Watch Compass: Point hour hand toward sun, halfway between hour hand and 12 o’clock indicates south (north of equator).
Vegetation Indicators: In northern climates, moss typically grows more heavily on north sides of trees and rocks where moisture persists longer.
Snow Patterns: Wind-blown snow forms cornices on lee sides of ridges, indicating prevailing wind direction for regional navigation.
🎒 Essential Wilderness Survival Kit: The Ten Essentials
Building an effective wilderness survival kit requires balancing weight, versatility, and redundancy for critical survival functions across diverse wilderness emergencies and environmental conditions.
The Ten Essentials represent the foundation of any wilderness survival kit, providing capabilities for the fundamental wilderness survival skills while remaining lightweight enough for day trips where most survival situations originate.
Your wilderness survival supplies must prioritize multi-use items that serve multiple functions while keeping pack weight manageable for extended carry during emergency situations.
| Essential Category | Primary Item | Backup Option | Weight | Critical Function |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Navigation | Map & Compass | GPS Device | 4 oz | Route finding |
| Fire | Waterproof Matches | Ferro Rod | 2 oz | Heat, signaling |
| Shelter | Emergency Bivvy | Large Garbage Bag | 6 oz | Weather protection |
| Insulation | Extra Layer | Emergency Blanket | 8 oz | Temperature regulation |
| Illumination | Headlamp | Backup Flashlight | 3 oz | Night visibility |
| First Aid | Personal Med Kit | Duct Tape | 6 oz | Injury treatment |
Survival Knife: Your Most Versatile Tool
Essential for wilderness survival techniques and emergency preparedness
A quality survival knife serves multiple functions: shelter construction, fire preparation, food processing, first aid applications, and emergency signaling when used with reflective surfaces.
Look for full-tang construction, 4-6 inch blade length, and high-carbon steel that holds an edge while remaining easy to sharpen with field stones.
✅ Multi-Purpose Survival Applications
- Shelter Building: Cut branches, strip bark, carve joints
- Fire Preparation: Split kindling, create feather sticks
- Food Processing: Clean game, prepare plant materials
- Tool Making: Carve spears, traps, cooking utensils
- Emergency First Aid: Cut bandages, remove splinters
❌ Knife Selection Mistakes
- Poor Steel Quality: Won’t hold edge or breaks under stress
- Hollow Handle Design: Weak construction fails when needed
- Oversized Blade: Difficult to control for detailed work
- Cheap Construction: Tang breaks during heavy use
- No Maintenance Plan: Dull knife dangerous and ineffective
🌲 Regional Survival Scenarios: Applying Skills to Real Environments
Michigan Wilderness Survival: Great Lakes Region
Primary Challenges: Rapid weather changes, dense forest navigation, seasonal temperature extremes, limited visibility
Specific Considerations: Lake-effect snow creates sudden whiteout conditions, swampy areas provide water but require purification, dense forest limits solar navigation methods.
For detailed winter-specific techniques, see our comprehensive winter survival kit guide.
Recommended Michigan Survival Approach:
- Debris hut construction using abundant hardwood leaves
- Water procurement from numerous streams and lakes
- Fire building with birch bark tinder and maple wood
- Navigation using ridge lines and water flow patterns
Desert Survival: Arid Environment Challenges
Primary Threats: Extreme heat, water scarcity, sun exposure, temperature extremes between day and night
Survival Priorities: Shade shelter construction, water conservation, night travel, heat injury prevention
Desert-Specific Techniques:
- Underground shelter to escape daytime heat
- Solar still construction for water procurement
- Rock reflection for fire starting
- Star navigation for night travel
Mountain Wilderness: High Altitude Survival
Environmental Factors: Altitude effects, rapid weather changes, steep terrain, limited shelter materials
Critical Skills: Snow cave construction, altitude acclimatization, avalanche awareness, cold injury prevention
High-Altitude Modifications:
- Wind protection becomes critical for shelter
- Water boiling time increases with elevation
- Solar radiation intensifies significantly
- Physical exertion limitations due to thin air
🍂 Food Procurement: Sustaining Energy for Extended Survival
Food procurement becomes important for survival situations lasting beyond one week, when body energy reserves begin affecting decision-making and physical capabilities.
Understanding safe foraging, basic trapping principles, and fishing techniques provides nutrition sources that extend survival time and maintain strength for rescue activities.
Safe Foraging Guidelines
Important for extended wilderness survival situations
Universal Edibility Test: When plant identification remains uncertain, test small amounts progressively: skin contact, lip contact, tongue contact, chew and spit, swallow small amount, wait for reactions at each stage.
This method takes 24+ hours but prevents poisoning from unknown plants. Never skip steps or test multiple plants simultaneously.
Common Edible Plants (North America)
- Dandelions: Entire plant edible, bitter but nutritious
- Plantain: Natural bandage, leaves edible raw or cooked
- Wild Garlic: Strong onion smell, bulbs and greens edible
- Acorns: Process to remove tannins, high calorie content
- Rose Hips: High vitamin C, available through winter
Basic Trapping and Fishing
Deadfall Trap Principles: Use gravity-powered traps triggered by animal movement. Requires understanding of animal patterns and food preferences rather than complex construction.
Improvised Fishing: Fashion hooks from safety pins, bones, or carved wood. Use insects, worms, or small pieces of bright material as bait. Focus on deeper pools where fish concentrate.
Survival Fishing Gear Foraging Tools🔧 Advanced Wilderness Survival Techniques
Advanced survival skills become valuable for extended wilderness situations or when basic techniques prove insufficient for challenging environmental conditions.
Cordage Making: The Foundation Tool
Essential for advanced wilderness survival techniques
Natural cordage enables trap construction, shelter improvements, tool making, and equipment repair using materials available in most environments.
Reverse Wrap Technique: Twist plant fibers clockwise while wrapping counterclockwise around existing cordage. This creates strong rope from weak individual fibers through mechanical advantage.
Best materials include inner bark from basswood, willow, or cedar, dried grass bundles, or fibrous plants like nettle and dogbane.
Primitive Tool Construction
Bow Making Basics: Select wood with natural curve, remove bark, taper ends gradually, string with strong cordage. Practice required for effective hunting tool.
Spear Points: Fire-harden wooden points or knap stone blades. Effective for fishing in shallow water or defensive purposes.
Emergency Communication
Ground-to-Air Signals: Create large X for medical emergency, I for injury, II for unable to proceed, arrow pointing toward civilization.
Mirror Signaling: Reflect sunlight using any reflective surface. Visible for 10+ miles to aircraft on clear days.
Smoke Signals: Add green vegetation to established fire for thick white smoke visible during daylight hours.
For emergency communication options, see our satellite phone guide.
📱 Integrating Modern Technology with Survival Skills
Modern survival technology enhances traditional skills rather than replacing them, providing backup options when primitive techniques prove challenging or conditions overwhelm basic methods.
Essential Survival Technology
Modern tools for wilderness survival and emergency preparedness
Personal Locator Beacons (PLB): Satellite emergency beacons that summon rescue regardless of cell coverage. Essential for solo wilderness travel in remote areas.
Water Purification Technology: UV sterilizers and advanced filtration provide safe drinking water faster than boiling methods while conserving fuel.
For comprehensive gear recommendations, check our survival camping gear guide and off-grid tech kit guide.
✅ Technology Advantages
- Reliability: Works regardless of skill level or conditions
- Speed: Faster results than primitive methods
- Accuracy: GPS provides precise location data
- Communication: Emergency rescue coordination
- Documentation: Photos aid plant identification
❌ Technology Limitations
- Battery Dependence: Fails without power source
- Weather Vulnerability: Electronics damaged by moisture
- Skill Atrophy: Over-reliance reduces manual capabilities
- Weight Factor: Additional gear burden
- Cost Investment: Expensive replacement if lost
Mental Preparedness: The Critical Eighth Essential
Often overlooked but crucial wilderness survival skills component
Psychological Resilience: Mental preparedness often determines survival success more than physical skills or equipment. Maintaining problem-solving ability under stress, adapting to changing conditions, and preserving hope during extended ordeals separates survivors from casualties.
Stress Inoculation Training: Practice wilderness survival skills while tired, cold, or hungry to simulate decision-making under duress. This builds confidence and muscle memory that functions when rational thinking becomes difficult.
Mental Survival Framework
- Acknowledge Reality: Accept your situation without denial or panic
- Prioritize Actions: Focus on immediate needs before long-term planning
- Celebrate Small Wins: Recognize progress to maintain morale
- Plan Multiple Solutions: Develop backup plans for critical needs
- Stay Connected to Purpose: Remember reasons for survival
🎯 Wilderness Survival Training: Building Competence Before Crisis
Effective wilderness survival training requires hands-on practice in controlled conditions before depending on these skills during actual emergencies when stress and time pressure compromise performance.
Whether you pursue formal wilderness survival training through certified programs or develop skills independently, consistent practice builds the competence that saves lives when plans go wrong.
Progressive Skill Development
Foundation for effective wilderness survival training
Backyard Practice: Master fire building, shelter construction, and water purification in comfortable conditions before attempting in challenging environments.
Day Trip Integration: Practice one survival skill per outdoor excursion. Build fires for lunch cooking, navigate using map and compass, identify edible plants.
Survival Training Progression
- Week 1-2: Fire building and basic shelter in good weather
- Week 3-4: Water location and purification methods
- Week 5-6: Navigation with map, compass, and natural methods
- Week 7-8: Integration practice during overnight camping
- Week 9-12: Challenging conditions and scenario practice
Mental Preparation
Stress Inoculation: Practice skills while cold, tired, or hungry to simulate emergency conditions when rational thinking becomes difficult.
Scenario Planning: Visualize specific emergencies and mental responses. Plan multiple solutions for common problems like sudden weather changes or equipment failure.
❓ Wilderness Survival Guide FAQ
What are the most important wilderness survival skills for beginners?
The most critical wilderness survival skills for beginners are shelter building, fire making, water procurement, and basic navigation. These four skills address the primary threats in survival situations: exposure, hypothermia, dehydration, and becoming more lost.
Start with shelter construction since exposure kills faster than dehydration. Master debris hut building in your backyard before depending on this skill in emergencies. Practice fire building with multiple methods until you can create fire consistently in wet conditions.
How long can you survive in the wilderness without food?
The Rule of Threes provides a general guideline: approximately 3 weeks without food. This varies drastically based on body fat, activity level, and environment, though individual factors like health condition and stress levels also affect this timeline. However, your decision-making ability and physical strength decline significantly after 3-7 days without food.
Focus energy on shelter, water, and rescue signaling rather than food procurement in short-term survival situations. Food becomes important only for extended survival scenarios lasting beyond one week.
What should I do first if lost in the wilderness?
Follow the STOP protocol: Sit down, Think about how you got here, Observe your surroundings, and Plan your next actions. Panic leads to poor decisions that worsen survival situations.
Stay where you are if people know your planned route and expected return time. Make yourself visible to rescuers by creating ground-to-air signals and staying in open areas. If you must move, mark your trail and travel toward known features like roads or rivers.
How do you find water in the wilderness safely?
Look for water indicators including green vegetation, animal trails, and the sound of flowing water. Follow terrain downhill toward valleys where water naturally collects. Check rock depressions, tree wells, and morning dew collection.
Always purify water before drinking by boiling for 3+ minutes, using purification tablets, or UV sterilization. Even clear mountain streams can contain harmful parasites like Giardia that cause severe illness.
What’s the best way to signal for rescue in wilderness emergencies?
Use the “rule of threes” for signaling: three whistle blasts, three mirror flashes, three smoke columns, or three ground signals arranged in triangle pattern. These indicate distress to rescuers.
Mirror signals work best during sunny conditions and can be seen 10+ miles by aircraft. Fire with green vegetation creates thick smoke visible during daylight. Personal locator beacons (PLBs) provide most reliable rescue coordination through satellite emergency services.
Can you build an effective shelter without tools?
Yes, effective shelters can be constructed using only natural materials. The debris hut design provides excellent insulation using a ridgepole framework covered with 3+ feet of leaves, pine needles, and organic debris.
Key principles include ground insulation to prevent heat loss, wind protection, and sizing the interior just large enough for your body to heat with body temperature. Location selection matters more than complex construction techniques.
What are essential wilderness survival tools for shelter building?
Essential wilderness survival tools for shelter building include a quality knife for cutting materials, paracord for lashing framework, and an emergency tarp or space blanket for waterproofing. However, effective shelters can be built using only natural materials.
A multi-tool provides cutting, drilling, and measuring capabilities in one compact wilderness survival tool. Practice building shelters with minimal tools to develop skills that work when gear fails or gets lost during emergencies.
What navigation tools are recommended for wilderness survival?
Recommended navigation tools include a topographic map of your area, baseplate compass, and GPS device with extra batteries. The map and compass provide reliable navigation regardless of battery life or satellite coverage.
Essential wilderness survival supplies for navigation also include a pencil for marking routes, protective case for maps, and backup compass attached to gear. Practice triangulation and bearing techniques before depending on these tools in actual emergencies.
📚 Essential Wilderness Survival Resources
The West Virginia Emergency Management Division provides official wilderness survival guidelines and search-and-rescue coordination information for outdoor emergency situations.
National weather services provide crucial forecast information for trip planning and emergency weather awareness that affects survival situation outcomes.
🏆 OTL Bottom Line: Your Complete Wilderness Survival Action Plan
Essential Skills Priority: Master shelter building and fire making first – these skills address the most immediate survival threats and provide foundation for all other techniques.
Best Training Investment: Practice the Rule of Threes framework with hands-on skill development in controlled conditions before depending on these techniques during actual emergencies.
Most Critical Gear: The Ten Essentials provide survival redundancy while remaining lightweight enough for day trips where most survival situations originate.
⚠️ Survival Reality Check: Knowledge alone doesn’t ensure survival – practice these skills regularly in progressively challenging conditions to build muscle memory and confidence that functions under stress.
Wilderness Survival Action Steps
- Week 1: Master debris hut construction and fire building basics
- Week 2: Practice water procurement and purification methods
- Week 3: Learn navigation with map, compass, and natural techniques
- Week 4: Integrate skills during day hikes and camping trips
- Ongoing: Practice scenario-based training in various weather conditions
Wilderness survival skills provide confidence and safety for outdoor adventures while building self-reliance that serves you in many life situations beyond emergency scenarios.
The key to effective wilderness survival lies in systematic preparation, progressive skill development, and understanding that survival success depends more on knowledge and mental resilience than expensive gear.
Always inform someone of your adventure plans and expected return time.
While these wilderness survival techniques provide crucial backup capabilities, proper planning and preparation remain your primary safety tools for any outdoor adventure.
- [Built-in 4 Charging Cables] This power bank is built with 3 output cables ( Type C*1 & iOS*1 & Micro USB*1) and 1 USB-A…
- [Advanced Wireless Charging] This portable charger supports advanced wireless charging, compatible with all wireless-ena…
- [Power 6 Devices at Once] This solar charger is also equipped with 4 ports (iOS input, USB A output, USB C input/output)…









Leave a Reply